This webpage serves as a comprehensive repository for device-specific supplementary materials, including Training guides and protocols, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), etc.
SCIC Device Tutorial
The following accordion part has separate items for each device.
This item is designed for NextSeq 2000.
NextSeq 2000 Manual and SOP for standard chemistry, SOP for kits with XLEAP technology
All training documents on the Illumina
Important Links:
- Molecular Biology of Illumina Sequencing
- Review of NGS Methods, and Illumina Sequencing
- BaseSpace Run Doc
- Sample Sheet Example1, Sample Sheet Example2
- How many (real) cycles does each kit have?
- Single Cell RNA Compatibility
- Steps of a run
- Training Web Page of Illumina
- Sequence Coverage Calculator
- Protocols
- Support Team Info
- XLEAP Technology Related Links:
- Why XLEAP Technology is faster : Video 1, Video 2 (longer)
- XLEAP Technology, history: Video
- An article
- A webinar
- NextSeq 2000 and XLEAP
Training and Supplementary Documents:
- Workflow Doc: It provides the speicifications of the device and kits and briefly demonstrates how to perform a run.
- Monitoring a run: This file elaborates how to evaluate run results and gives trips on how to optimize a custom library run.
- Dragen Intro: It provides a background info about the Dragen on NextSeq 2000.
- Proactive Doc: Proactive monitors all runs in a specific NGS device. The doc summarizes how to use it.
Contact:
- Tonya Brown:Field Application Scientist; cbrown7@illumina.com
- Taylor Stone; District Inside Sales Representative-Midwest; tstone@illumina.com
- Logan Silber; Sequencing Sales Specialist; lsilber@illumina.com
- Kevin Fitzgerald; Sr/ Inside Sales Representatibe; kfitzgerald1@illumina.com
Related Videos:
A demonstration of our new NextSeq 1000/2000 XLEAP-SBS cartridge preparation ‘lift and release’ step
NextSeq2000: Run Quality and Best Practices
How to remove the components of a cartridge for recycling.
Introduction to NextSeq 2000
How to Generate Sample Sheets for Local Run
How to Generate Sample Sheets for Local Run
How to requeue analysis for a NextSeq2000 run
How to power cycle NextSeq 2000

This item is designed for MiSeq.
Important Links:
- Molecular Biology of Illumina Sequencing
- Sequencing: Introduction to Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS)
- Review of NGS Methods, and Illumina Sequencing
The washing steps are used for the maintenance of the device
Here are the types of washes for MiSeq:
Post-Run Wash: After every sequencing run.
1X wash step: 0.5% Tween 20 wash solution (Wash volume: 17.25 ml)
a. Add 6 ml wash solution to each reservoir of the wash tray.
b. Add 350 ml wash solution to the 500 ml wash bottle.
Maintenance Wash: Required every 30 days (instrument will begin warning user that maintenance wash is required at 30 days and it will prevent user from sequencing if maintenance wash has not been completed within previous 45 days).
3X wash steps: 0.5% Tween 20 wash solution (fresh for each wash step) (Wash volume: 51.75 ml).
a. Add 6 ml wash solution to each reservoir of the wash tray.
b. Add 350 ml wash solution to the 500 ml wash bottle.
Standby Wash: Prepares instrument for idle mode (if instrument unused for > 7 days), and every 30 days if instrument remains idle.
2X wash steps: 0.5% Tween 20 wash solution (fresh for each wash step) (Wash volume: 46 ml).
a. Add 6 ml wash solution to each reservoir of the wash tray.
b. Add 350 ml wash solution to the 500 ml wash bottle.
When the standby wash is complete, the instrument is in standby mode and a message appears on the home screen indicating the status of the instrument.
When the instrument is in standby mode, a maintenance wash must be performed before a sequencing run can be initiated.
Note:
- If you are running your instruments frequently (2-3 runs/week) It is recommended that the power cycling should happen once a week.
- If running less frequently than that, please power cycle once in two weeks. If running rarely, please power cycle before each run.
Power Cycle: In every 2 weeks, it is necessary. Please watch the following video.
Training Video:
- A complete MiSeq run
- How to denature and dilute libraries and spike in PhiX
- How to prepare (thawing, mixing, etc.) all reagents (cartridge, buffer, flow cell) before the run

Explore the P2 Solo Training Hub to elevate your sequencing skills. Dive into expert-guided tutorials and unleash the potential of NGS research.
Details: The P2 Solo is a compact, cost-effective sequencer, offering a more budget-friendly entry point compared to its competitors. Similar to other ONT instruments, it excels in long-read sequencing, spanning from 20 bases to over 4 Mb. Users have the flexibility to run each flow cell independently or simultaneously, allowing for the multiplexing of up to 96 samples in a single run. The P2 Solo supports various applications, including direct RNA sequencing, direct methylation detection, and chromatin conformation capture with Pore-C. When both flow cells are utilized, data output can reach up to 580 Gb, with expected outputs per flow cell as follows: 100-200 Gb for native gDNA reads (read N50 - 25 kb), 50-100 Gb for ultra-long native DNA reads (>50 kb read N50), and >200 Gb for metagenomic samples (read N50 ~ 10 kb).
Contacts:
- Gabi Saukeviciute; Inside Sales Specialist; gabi.sauke@nanoporetech.com; (678) 4697682
- Maddy Hartley, Field Application Scientist-Midwest; maddy.hartley@nanoporetech.com
- Bron Daniel; Account Executive-Great Lakes West Territory; bron.daniel@nanoporetech.com
- Luis Salazar; FAS; Luis.Salazar@nanopore
Videos
How it works
- How to design a NanoPore Sequencing Experiment
Training Video:
- How to load PromethION Flow Cell
- Extract high quality DNA and RNA
- How to select the right library prep workflow for your experiment
- How to perform tumour and normal sequencing
- How to get started with data analysis
- Advances in duplex basecalling and how to achieve Q30
More videos related to data analysis: Video 1, link 1, NanoPore 101
Cool topics:
- Liquid Biopsies
- Targeted sequencing
- R9 and R10 Chemistry (Q30 possible?)
- Master Classes: 2022
This item is designed for TapeStation.
Agilent 4200 TapeStation System Manual, SOP, the consumables and reagents
- How to run the TapeStation.
- How to evaluate the TapeStation results.

This web page is dedicated to CFX384 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System located in Single Cell Immunophenotyping Core.
Although the Maestro & device manual and its SOP contain enough info to operate the device, the following training videos are essential to be able to completely use the device.
Training Sources for the device and its software called Maestro
- First set-up
- How to set up the protocol by using Maestro
- How to set up the plate by using Maestro
- How to set up biological and technical replicates in CFX Manager
- How to analyze data in CFX Manager
Alternative Links:
- Plate Set-up
- Reference genes Set-Up
- Data analysis and Statistics
- Graph Customization, Annotate and Export
- How to design a qPCR assay
Quick Guides (pdf documents):
- CFX Manager Software Protocol
- CFX Manager Software Plate QG
- CFX Manager Data Analysis QG
- CFX Manager Software Gene Expression Analysis
- qPCR Assay Design QG

This section is generated for 10X Genomics Chromium X.
10X Genomics Chromium X Manual and SOP
Important Links:
- 10X Genomics Chromium X Offical Web Page
- 10X Chromium X Documents
- Background Information about Single Cell Sequencing
- A webinar on its applications: presentation, video link (code: +B%$1eL2)
- Training Videos
- Single Cell Sequencing Short Video
Training Videos:
- Loading Chromium Next GEM Chip G
- 10X Chromium run
- Checking the droplets after 10X Chromium run
There are a lot of visual experiments in JoVe which is a prier reviewed scientific video journal. For example
Profession Contact:
1. Grace Snyder, Ph.D. (she/her); Field Application Scientist, Illinois Metro; grace.snyder@10xgenomics.com; Mobile: 925 596 8522
2. Jason Karpus, Sales Representative; jason.karpus@10xgenomics.com

NextSeq 2000:
1. What are the manual loading volume and concentrations?
Normally, the library is automatically diluted and denatured by NextSeq 2000.
Loading volume is 20 ul.
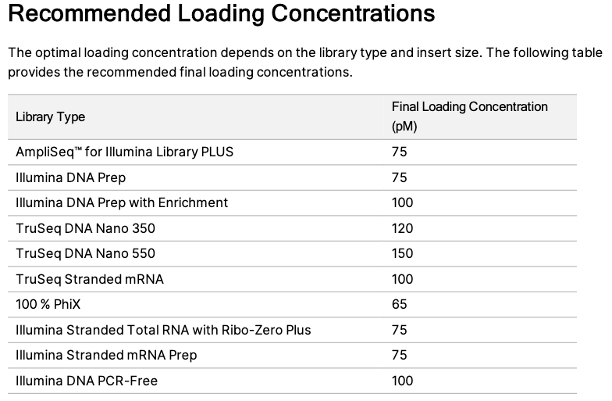
For manual dilutions, please use the following numbers:

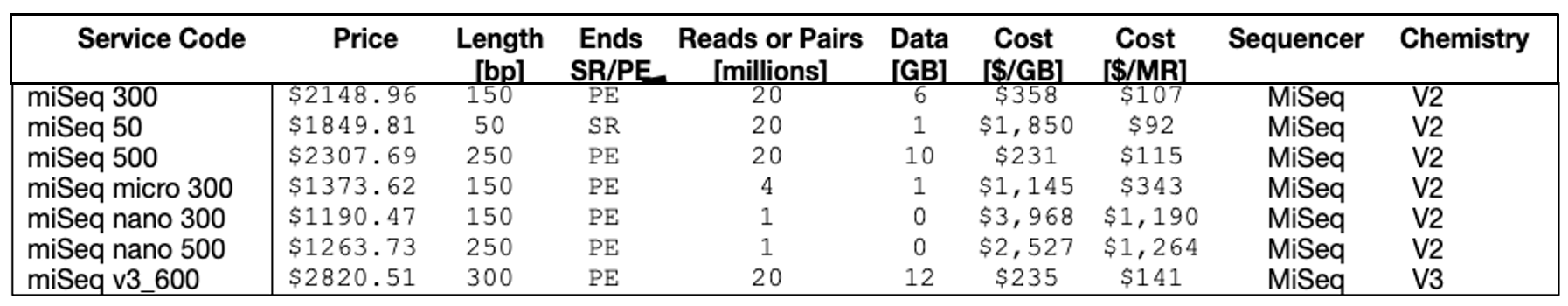
2. What is the cost analysis of MiSeq kits?
3. How is the integrated dry cartridge different from the reagents of the MiSeq™ or NextSeq 550 Systems?
The NextSeq 1000 and NextSeq 2000 Systems are referred to as dry instruments because they use cartridges that integrate all fluidic components necessary for amplification and sequencing. In contrast, MiSeq and NextSeq 550 systems contain separate fluidics within the instrument. The integrated cartridge helps to reduce the possibility of cross-contamination. Fluid waste can be purged back into reagent cartridges for easy disposal and multiple plastic components in the cartridge can be easily separated from the waste components and recycled.
4. Do I need to know the specific flow cell cluster density? (NextSeq 2K)
Patterned flow cells consist of a nanowell substrate with billions of ordered wells. The NextSeq 1000 and NextSeq 2000 Systems use patterned flow cells, which result in a fixed cluster density, even if all nanowells are not occupied. Compared to nonpatterned flow cells, the uniform cluster sizes enable optimal spacing and increased cluster density. In these systems, monitoring the cluster percent passing filter is a better measure of potential cluster occupancy.
5. What are the considerations for switching to the patterned flow cell technology? (NextSeq 2K)
The patterned flow cell technology used by the NextSeq 1000 and NextSeq 2000 Systems is a large improvement over previous technologies due to the ability to avoid overclustering. However, some assay optimization will likely need to take place, especially for custom and third-party library preparation methods. Illumina support specialists are prepared to help every step of the way, from establishing a robust workflow and evaluation process to offering a 1:1 consultation with a field application specialist, or the ability to send samples to an Illumina customer solutions lab.
6. What are the storage conditions for NextSeq 2K consumables?
NextSeq 550 System consumables have a 3-month shelf life. NextSeq 1000 and NextSeq 2000 System consumables have a shelf life of 6 months.
7. How to calculate the concentration of PhiX for MiSeq and/or NextSeq runs?
The PhiX Control v3 Library (commonly referred to as PhiX, FC-110-3001) is derived from the small, well-characterized bacteriophage genome, PhiX. It is a concentrated Illumina library (10 nM in 10 µl) that has an average size of 500 bp and consists of balanced base composition at ~45% GC and ~55% AT. Due to its balanced nucleotide composition, the PhiX Control v3 Library is also an ideal sequencing control (typically with ≥ 1% spike-in) for run quality monitoring; e.g. cluster generation, sequencing, and alignment (more info). Please quantify the concentration of PhiX using Qubit before the spike-in. The following converter can be used to convert ng/ul to nM: NanoMolar Converter.
8. Is it possible to directly download the runs in our BaseSpace to our RCC account?
Yes, it is. BaseSpace Sequence Hub Command Line Interface (CLI) helps you to quickly download your runs to RCC. Please watch the video and check the guide file.
9. How to download fastq files from our BaseSpace account to our RCC account?
Please watch the video and check the guide file.
10. How to convert mass (ng) per µl DNA to fmol per µl DNA (needed for PromethION Solo Runs)
Please use the following link: https://nebiocalculator.neb.com/#!/dsdnaamt
Supplementaries:
Videos:
- Intro to MinION
- Intro to MinION M1kC
- How to run MinION M1kC
- Priming and Loading your MınION flow-cell
Note: Other videos that explains how to prime and load a flow cell, Video 1, Video 2,
- Priming and Loading your Flongle flow-cell
How to connect M1kC to a PC
How to wash a MinION Flow Cell
Important Links:
- The Company Web Site
- Device Manual
- Training Notes
- Reagent Manuals: Level 1,
- Reagent Fees
- Assays and Sample Volumes: Doc1
Related Videos:
Device Intro Videos
Introduction to Device Operation (Video1)
How to Initiate a Requisition for a New Sample
Important Notes:
-
Contacts: Kelly Birmingham, kbirmingham@alfawassermannus.com, Director of Client Services; John Husted, jhusted@alfawassermannus.com, Business Development Manager; customerservie@awdt.us
Data Management:
Data Transfer Methods for Cloud Environments
-
Globus:
- A robust file-sharing and transfer service.
- Users can schedule transfers after data generation by P2Solo or M1kC.
- Ensures efficient and reliable data movement.
-
Samba:
- An easy data management method, but not recommended for privacy reasons.
- Users can visualize the cloud folder in the directory, transfer data, and remove it afterward.
-
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol):
- A secure alternative to FTP.
- FileZilla, a free and open-source FTP application, facilitates data transfer.
- Best practice: Transfer data from local folders to cloud-based storage for redundancy, collaboration, and secure analysis access.
Links
Videos:
- Globus
- Samba
- Filezilla
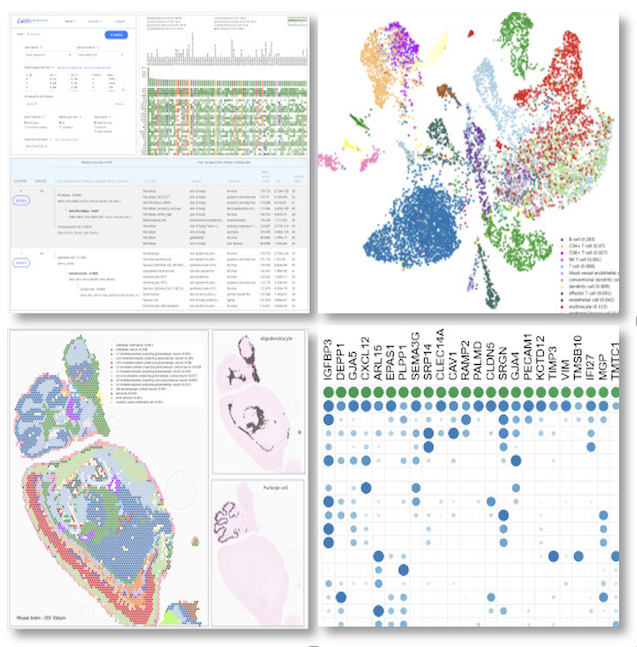
SCIC core offers full enterprise access to CellKb, the world’s largest manually curated cell type marker database.
What it CellKb?
CellKb is a comprehensive platform for automatic cell type annotation, prediction and biomarker discovery, which is fast and accurate cell type prediction at scale using our knowledgebase, proprietary algorithms and user-friendly interface. It is designed to support advanced research needs in transcriptomics and single-cell analysis.
What does CellKb do?
Key Features for Core Users:
| Key Features | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Cluster Annotation and Cell Type Prediction |
|
| Spatial Deconvolution |
|
| Single-Cell Annotation |
|
| Bulk Cell Type Enrichment |
|
| Consensus Signatures and Biomarker Discovery |
|
.
Bioinformatician Insight
"CellKb generates accurate cluster annotations for single-cell data, removing the need for manual curation. It draws from thousands of curated signatures across studies with high-quality datasets, allows filtering by source organ and disease state, and returns fine-grained cell type annotations along with two parent-level classifications. This makes cluster annotation more reliable and broadly scoped than manually compiling reference datasets for marker comparison or dataset projection." Maggie Clevenger
How can a User use the Service?
- Please email the following contact: ciic-singlecell@uchicago.edu
- We generate an enterprise account for you and you start
Why Choose CellKb?
CellKb empowers your research with expertly curated, harmonized cell type signatures and robust annotation tools. Here’s what sets CellKb apart:
- Expert Manual Curation: Marker gene sets are meticulously gathered from high-quality publications, focusing on both single-cell and select bulk RNA-seq or microarray studies.
- Deep Annotation: Each gene set features extensive cell type, anatomical, and disease data linked to the original publication, providing highly contextualized results.
- Standardization & Data Harmonization: All gene sets use unified gene naming and standardized ontologies for cell types, tissues, and diseases, ensuring reliable comparisons across datasets.
- Reliability Scoring: Every cell type signature is assessed for reliability based on its similarity to other references, giving you confidence in your results.
- Canonical Markers: Includes key reference genes used for cell type identification in scientific literature.
- Advanced Search Algorithms: Proprietary ranking quickly finds the best matching cell type signatures for fast, accurate annotation.
Premium Benefits for Core Users:
- Unlimited Analyses: Run as many cell type annotation and prediction tasks as your projects require—no limits.
- Top 100 Cell Type Matches: Receive the most comprehensive lists of cell type matches, helping you explore all candidate cell identities.
- Full Feature Access: Unlock all annotation, search, deconvolution, enrichment, and integration capabilities.
- Commercial Use License: Use CellKb confidently for commercial projects and proprietary research.
- Priority Support: Enjoy dedicated technical help to resolve queries quickly and keep your workflow running smoothly.